

Introduction: Water scarcity poses a significant challenge to communities worldwide, prompting the exploration of innovative solutions to meet the growing demand for clean drinking water. One such groundbreaking technology that has gained attention is the extraction of potable water directly from the air. This process, known as atmospheric water generation, holds the promise of transforming the most abundant resource around us – the air – into a sustainable and reliable water source.
How It Works: Atmospheric water generation typically employs a two-step process: condensation and purification.
Condensation: Specialized machines, known as Atmospheric Water Generators (AWGs), draw in air and cool it, causing moisture to condense into water droplets. This condensed water is then collected.
Purification: The collected moisture undergoes a thorough purification process to ensure it meets or exceeds drinking water standards. Filtration, UV sterilization, and other advanced purification methods are employed to remove impurities and contaminants, resulting in crystal-clear, safe drinking water.
Benefits of Air-to-Water Technology: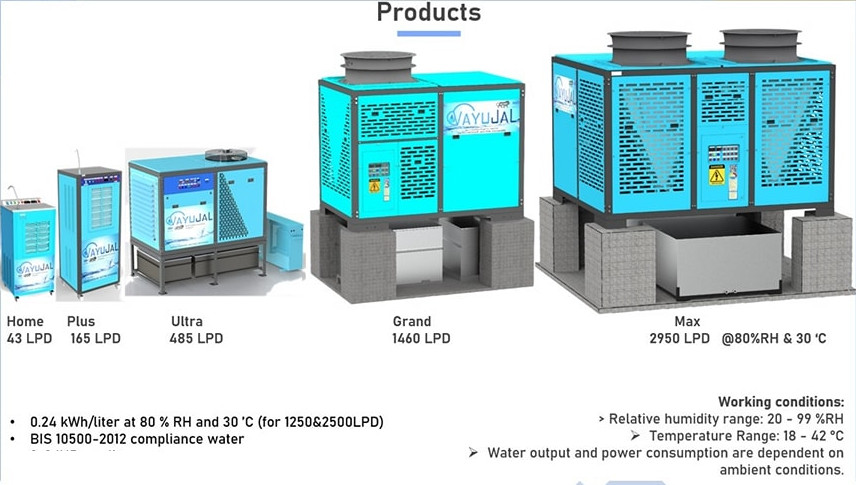
Independence from Traditional Sources: Air-to-water technology provides an alternative water source, reducing reliance on traditional sources such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
Resilience in Arid Regions: This technology offers a lifeline in arid and water-stressed regions, where conventional water sources are scarce. It can be particularly impactful in mitigating the effects of droughts.
Sustainability: Some systems are designed to be solar-powered, reducing the environmental impact and making the technology more sustainable. Harnessing renewable energy for water generation contributes to a greener and more eco-friendly solution.
Disaster Response: Portable atmospheric water generators can be quickly deployed in emergency situations, providing immediate access to safe drinking water during natural disasters or humanitarian crises.
Challenges and Considerations: While air-to-water technology holds immense potential, it's important to address challenges such as energy consumption, scalability, and initial setup costs. Additionally, research and development efforts should continue to optimize efficiency and make the technology more accessible globally.
Conclusion: As water scarcity continues to escalate, the ability to extract drinking water directly from the air offers a transformative solution. Air-to-water technology represents a beacon of hope for communities facing water challenges, providing a reliable, sustainable, and innovative source of pure drinking water. Embracing and investing in this technology can contribute significantly to building a resilient and water-secure future for all.